Utah Fish and Game Advisories
The Utah Department of Environmental Quality (UDEQ) and the Utah Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) work together to monitor the presence of chemical toxins in fish and waterfowl in Utah waters. Even when present in the water in extremely small amounts, some chemicals tend to accumulate in fish and game tissues because they absorb contaminants from the water and sediment and from the food they eat. For fish, the amount of contaminants they accumulate depends on the species, size, age, and sex, and the feeding area of the fish.
Generally, older and larger fish accumulate the most contaminants. Since fish accumulate many contaminants in their fatty tissues, certain species with higher oil or fat content can pose more risk than others when both inhabit polluted areas.
Fish consumption advisories are recommendations by UDEQ and DHHS to limit or avoid eating certain species of fish or waterfowl from local waters due to potential health risks from contaminants.
Some fish may not be safe to eat because they accumulate environmental contaminants from the water which they live and eat. Women who are pregnant, may become pregnant, or are nursing should be very careful about the fish that they eat.
Utah public health officials issue fish consumption advisories when contamination levels are unsafe. The advisories outline recommendations for limiting intake of specific fish at specific locations.
Waterfowl consumption advisories are for waterfowl such as ducks or geese that are harvested from the Great Salt Lake marshes when there are elevated levels of mercury detected.
For more information visit the UDEQ Frequently Asked Questions page.
There are 5 toxins that make up the majority of advisories:
- Mercury
- Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)
- Chlordane
- Dioxins
- Dichloro-Diphenyl-Trichloroethane (DDT)
Current advisories for fish in Utah are for mercury and PCBs; while advisories for waterfowl are only for mercury.
Contaminants tend to concentrate in the fatty tissue, so proper cleaning and cooking techniques can significantly reduce levels of PCBs, dioxins, chlorinated pesticides and other organic chemicals. Larger fish tend to have higher concentrations, eating smaller fish will reduce your exposure to contaminants. Proper cleaning and preparation of fish can also reduce the chance of consuming chemical contaminants.
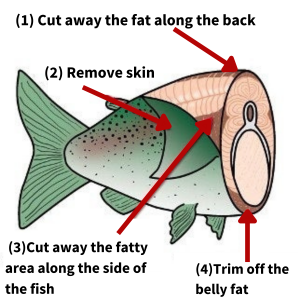
Remove all skin from the fish (1). Cut away any fat above the fish’s backbone (2). Cut away the V-shaped wedge of fat along the lateral line on each side of the fish (3). Slice off fat belly meat along the bottom of the fish (4).
Bake or broil trimmed fish on a rack or grill so some of the remaining fat drips away. Discard any drippings; do not eat drippings or use them for making sauces or gravy. Eat only the fillet and discard other tissues including bones.
Note: You cannot remove heavy metals by any cleaning or cooking methods; these techniques will not reduce or remove unsafe levels of mercury from fish.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women, women of child bearing age and children are considered sensitive populations and should carefully follow consumption advisories for their group.
For more information, visit the EPA Fish Consumption Advisories page.
Fish advisories have been issued in Utah due to high levels of heavy metals (arsenic and mercury) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), a type of organic contaminant. You can visit UDEQ’s website for a list of current fish advisories by species, county, or water body. You can also search advisories by each contaminant by clicking on the links below.
In 2022, Utah APPLETREE and UDEQ analyzed mercury in fish tissue from various locations in Utah. Some locations have new consumption fish advisories for certain species. Click on the locations below to see a monthly fish consumption recommendation for the species listed.
Big Sandwash Reservoir - Smallmouth bass, Walleye, and Yellow perch
Cottonwood Reservoir - Black bullhead and wiper
Electric Lake - Cutthroat trout and Tiger trout
Newcastle Reservoir - Larger wiper, Rainbow trout, Smallmouth bass, and Small wiper
Newton Reservoir - Largemouth bass
Pelican Lake - Lake bluegill and Largemouth bass
Rockport Reservoir - Smallmouth bass
Starvation Reservoir - Smallmouth bass
Steinaker Reservoir - Blue gill, Brown trout, Largemouth bass, and Rainbow trout
Anuncios de pescado en Español
¿Necesitas la guía para el consumo seguro de pescado en español? Haga clic en los enlaces donde pescará para leer la guía.
Reserva de Agua Big Sandwash - Lobina de boca pequeña, Pez leucoma, y Perca flavescens
Reserva de Agua Cottonwood - Pez gato y Lubina rayada
Reserva de Agua Currant Creek - Trucha tigre
Lago Electric - Trucha degollada y Trucha tigre
Reserve de Aqua Newcastle - Lubina rayada grande, Trucha arcoíris, Lubina, Lubina rayada pequeña
Reserva de Agua Newton - Lobina negra
Reserva de Agua Starvation - Lobina de boca pequeña y Pez leucoma
Lago Pelicano - Pez sol y Lobina negra
Reserve de Agua Rockport - Lobina de boca pequeña
Reserva de Agua Steinaker - Pez sol, Trucha marrón, Lobina negra, y Trucha arcoíris
Inorganic Arsenic in Fish from the North Fork of the American Fork Canyon (2003)
Contaminants in Fish from Silver Creek (2004)
Inorganic Arsenic in Fish from the North Fork of the American Fork Canyon (2004)
An Evaluation of Mercury Concentrations in Waterfowl from the Great Salt Lake 2005)
Contaminants in Fish from Cutler Reservoir (2005)
Contaminants in Fish from Gunlock Reservoir (2005)
Contaminants in Fish from Strawberry Reservoir (2005)
Contaminants in Fish from Utah Lake (2005)
Contaminants in Fish from Yuba Lake (2005)
An Evaluation of Mercury Concentrations in Ducks from The Great Salt Lake (2006)